As an Amazon Associate, we earn from qualifying purchases. We may also earn commissions if you purchase products from other retailers after clicking on a link from our site.
Catamarans are the perfect backdrop to a relaxing fishing excursion, with sails in the wind as you reel in 50-pound striped bass. But when the gusts pick up and shift directions, you’ll find yourself weathering uncharted territory where reefing and speed are unlike a classic monohull. Sailing a catamaran upwind and downwind requires a skill set much different from the classic one hulled sailing.
To sail a catamaran upwind, maintain high speeds, center the mainsheet, limit angles to 45-60°, lose unnecessary weight, upgrade to Kevlar sails and daggerboards. To sail a catamaran downwind, maintain 160-170°, use asymmetrical spinnakers, reef when winds exceed 15 knots, and jibe.
Downwind gusts can help a catamaran surf down waves, something that is extremely exciting. However, facing those dreaded upwind breezes (especially without daggerboards) can signal the end of a soothing Mediterranian adventure. To learn how to sail a catamaran upwind or downwind, read on!
How Sailing a Catamaran Is Different Than Monohulls
Multihull vessels like catamarans respond very differently to rough surfs, gusting winds, and shallow waters. If you’re still questioning, “What’s the difference?” here’s your answer.
Compared to classic monohull boats, catamarans are:
- More stable — at sail and when anchored — and less likely to heel or rock from side to side.
- Less responsive to waves and winds (detecting these requires keen observation skills).
- Likely to struggle when sailing into the wind.
- Harder to tack (high speeds are essential to avoid losing momentum)
Traditional yacht enthusiasts quickly learn that sailing a catamaran is smoother, though stiff headwinds and choppy surf are more challenging to overcome. Learning to master upwind and downwind catamaran sailing is essential to get the most out of your trip
If there’s one debate looming over the sailing community, it’s the age-old catamaran versus monohull discussion.
What is the difference between cats and monos?
The UPWIND Catamaran Sailing Guide
Sailing upwind means you’re cruising your catamaran toward the wind (i.e., Traveling east against westward-blowing gusts). This added wind resistance makes it more challenging to reach your destination swiftly and safely, as upwind journeys could come with:
- Relentless sail luffing (fluttering like a bedsheet on a clothesline)
- Slowed speeds and VMG (velocity made good)
- Deep-digging bows in waves
- Bridge deck slamming
Preparing for an upwind journey means taking the path of least resistance and the “long way home.” To survive your next upwind sail unscathed, follow these tips:
Maintain High Speeds
Thirty-knot gusts at-sea, high speeds, and a Leopard 44 might sound like a recipe for disaster. But a catamaran’s multihull design allows for lower capsize risks and less heeling in rougher conditions. It’s far gentler on the vessel to maintain momentum than to build throttle against heavy winds.
Sailing a catamaran upwind requires sail, chart plotter, and daggerboard monitoring. The video below discusses upwind sailing tips as your catamaran’s bow faces 20-knot gusts.
Limit Angles to 45–60°
A straight line is undoubtedly the shortest pathway to your on-shore destination, but sailing your catamaran directly into the wind will land you in the dreaded “no-go zone.” That is, sailing into 15-knot wind gusts directly, draining all forward momentum (unless motoring), and being unable to steer responsively.
The point of sail “sweet spot” for catamarans sailing upwind is between 45 and 60°. This tight range will keep the bow headed in the right direction — toward a particular cove or dock — without cutting throttle (too direct) or over-inflating the sails (too perpendicular).
An onboard flag can help you accurately detect your current point of sail (there are of course electronic aids as well). You should adjust the sails intentionally to ensure the perfect angle:
- Slowly let out your sail.
- Wait for the telltale to begin luffing (flapping in the wind).
- Gently tug it back until the telltale flapping stops.
Upgrade to Kevlar Sails
Catamarans are impressively resistant to heeling where dainty monohulls might capsize. But instead of “giving” with the wind, a catamaran’s classic polyester sails will resist 30+ knot gusts almost entirely. Even the highest-tenacity Dacron sailcloths will develop wear and tear, performance-reducing distortions, or irreversible breakage in heavy winds.
Investing in heavy-duty Kevlar sails can create stiffer and more damage-proof sails that can better handle upwind excursions. Upgraded catamaran sail cloths can help you travel a crisper pathway at a close-hauled 45° without overcompensating at the wheel.
Select a Daggerboard Catamaran
Daggerboards are retractable vertical keels attached to a catamaran’s underbelly. These large, below-deck protrusions can prevent or limit any leeway in exceptionally windy conditions.
Daggerboards vs Centerboards explained!
In other words, daggerboards will keep your catamaran from drifting with the wind or falling off course. The $30,000 higher price tag is undoubtedly off-putting, especially when proper tacking technique might render them useless. But the benefits are substantial:
- Sailing 1-2 knots faster than a standard keeled catamaran
- Traveling 5-7° closer to the no-go zone
- Reaching your upwind destination quicker and with less dramatic tacking
Catamarans with daggerboards installed are more reliable and accurate when traveling upwind. But these built-in keels require proper care to prevent grounding or lurching into a reef. Until your sea voyages bring you upwind, keep your daggerboards raised.
Clean Hulls
Aside from trimming the sails and staying in the close-hauled zone, there’s only so much you can do onboard to better tackle an upwind voyage. But what about beneath the water’s surface? A dirty underside can wreak havoc on your catamaran’s all-around performance — cutting RPM by 1,000, draining fuel efficiency, and slashing your maximum speed by several kts.
Keeping your catamaran hulls free of barnacles, grime, and fouling can make your upwind travels far less treacherous. Revive upwind sailing potential by:
- Spraying the bottom clean with an on-land hose
- Scrubbing the slimy waterline with a soft brush or sponge
- Dislodging caked-on algae with a plastic putty knife
- Applying a fresh coat of antifouling paint
Scrub your catamaran’s underbelly clean at least four times a year, though monthly is preferred for maximum performance. You’ll quickly notice a swifter, cleaner, and smoother journey the next time you take your catamaran up the coast.
Trim the Sails & Center the Mainsheet
“Trimming” the sails is a beginner’s catamaran cruising skill designed to improve speed and better catch the breeze. By changing the angle of the sails and adjusting line tension, you can evade sail luffing and add several knots to your voyage — especially upwind. It takes practice to adapt your sails to the wind speed and direction, so here are the catamaran sail trimming basics:
- Lock the mainsheet and position the boom so that it’s somewhat leeward (further away from the wind gusts).
- As you veer away from the wind, slightly ease the traveler and monitor the telltales.
- Start slowly easing the mainsheet when you’re on a beam or reaching (when the catamaran is at the right angle to the wind).
- Keep an eye on the telltales and watch for differences between leward and windward side (bluffing or flopping).
As you go through the classic trial and error process, don’t forget to keep the mainsheet centered — or as close to the center as possible. Otherwise, turning the winches in 18+ knot winds will require superhuman strength to get back on track, complicating your sail.
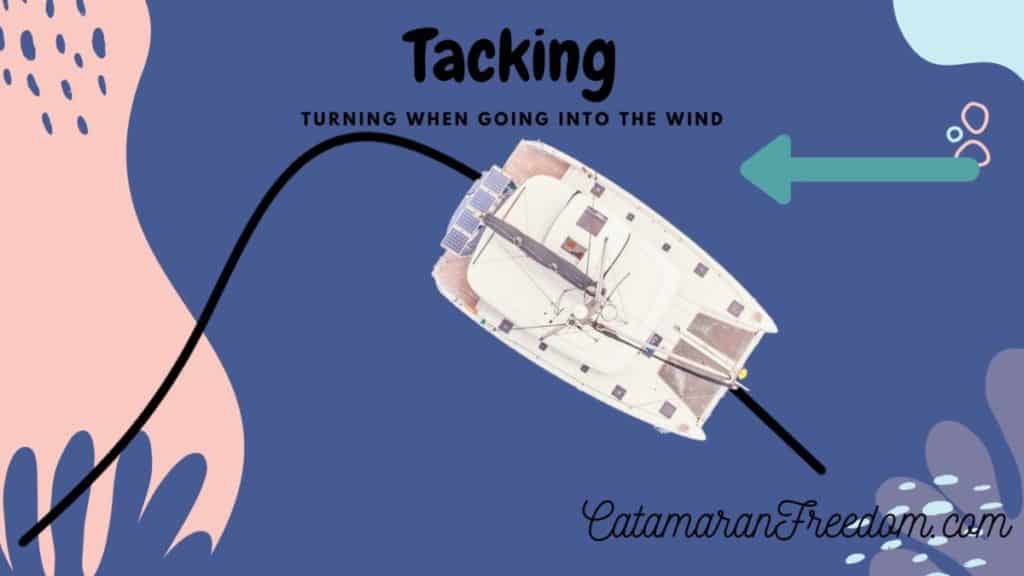
Tack

Steering clear of the no-go zone (straight into the wind) will keep your catamaran from stalling and your sails from flapping around and potentially increasing wear. But you’ll never arrive at your coordinates if you’re staying on a strict 45° path in one direction. This is where skilled catamaran sailors begin “tacking”, the art of turning your boat with the wind on your bows.
When you tack on a sailboat, you’re forcing the bows into the wind’s direction (no go zone). Tacking redirects the bow to the opposite 45° angle — from 3 o’clock to 9 o’clock — and creates a zig-zag formation or subtle 90° turns through the water. Proper tacking requires a skilled crew on larger catamarans but can be a solo pursuit. Here’s how to do this maneuver carefully:
- Start by sailing as close to the close-hauled territory as possible (within 40-45°).
- Choose a heading 90° away as your turn “destination.”
- Alert the crew to the tacking (if applicable).
- Slowly release the loaded jib sheet and begin pulling the lazy sheet inward.
- Steer the catamaran into the turn while maintaining speed (don’t speed up or slow down).
- Allow the sail to backfill to assist with the pivot.
- Release the jib sheet (watch your fingers, as the line releases quickly).
- Tighten the jib sheet on the opposite side and feel the wind start powering the boat.
Tacking is a challenging sailing concept to master. But it’s also the only way to sail upwind efficiently.
Turn On the Motor
A traditional, motor-free catamaran cruise can be soothing if there’s no destination in mind. However, the sails become inefficient against 15-knot winds when your preferred snorkeling spot is several miles directly into the wind. The best way to sail upwind is by turning to your catamaran’s twin diesel engines and hitting the throttle. Even cranking the engine to half-speed can ignite your speed by 1-2 knots and improve the course by up to 20°.
The DOWNWIND Catamaran Sailing Guide
Sailing downwind means you’re cruising in the same direction as the wind’s blowing (i.e., Journeying north alongside north-blowing winds). This extra momentum can generate higher speeds on a run, though the consequences of unpredictable downwind exist. Spinnakers becoming tangled around forestays or spinnaker collapse are looming concerns in high winds.
Downwind sailing is the catamaran sailors’ favorite direction, and thats why most people circumnavigating the globe is travelling with the tradewinds going west!
How to circumnavigate the world
Downwind trips are much more straightforward for novice sailors, but there are techniques for building speed and learning more about your boat. To better handle your next downwind sail like an expert, follow these tips
Use a Screecher or Asymmetrical Spinnakers
Spinnakers are a special type of sail ideal for downwind runs. Unlike a mainsail or jib that luffs in the wind, spinnakers inflate like a balloon and give maximum power at around 90-160° angles. These ultra-lightweight, colorful sailcloths come in two varieties: Asymmetrical and symmetrical. Most yachters attach asymmetrical spinnakers or screechers to their catamarans because they:
- Work well in close-hauls, beams, and broad reaches
- Boost speed by about 2 knots
- Resist damage in 25-knot downwind gusts
- Are quite versatile
The latest spinnaker tends to have more volume when tacked to the windward bow. These new designs allow them to catch more wind and pick up speed at nearly all deep, downwind angles (except directly at your aft).
Sailing a catamaran downwind isn’t quite as simple as easing the sails and cruising. The video below explains the catamaran difference when traversing the sea with the wind at your aft.
Choose the Right Angle
Sailing a catamaran directly downwind sounds like a decent strategy for picking up some momentum. But because catamarans travel faster with the wind at their sails, a less direct point of sail can maximize your velocity made good (VMG).
The proper point of sail for downward cruises is in the broad reach position — ideally between 160 and 170°, though up to 90° can be somewhat effective. This 10-20° off-center angle is slight but can boost your maximum speeds by a few knots.
Reef at 15 Knots
Though catamarans don’t heel or spill wind like monohull ships, the high wind pressure cues are more challenging to detect. Sailing behind 15 or even 20-knot gusts can overpower even the sturdiest sails when you jibe. Reducing your sail surface area and allowing more wind to flow through — reefing — will reduce speed(usually) and increase safety.
Always keep an eye on your anemometer while sailing downwind in windier conditions. Once it’s registering 15-20 knots, here’s what you should do:
- Reduce the mainsail’s pressure by loosening the mainsheet and repositioning the traveler leeward (away from the wind).
- Take the pressure off the boom vang.
- Lower the main halyard and hook reefing point #1 on the proper hook.
- Pull the reefing line manually (or with a winch).
- Put more tension back on the halyard and boom vang.
Time is of the essence while reefing downwind, and one reef might not be enough if you’re sailing into a squall. Be prepared for a second or third reef when winds measure 25 and 30 knots, respectively. If winds exceed 30 knots, remove the jib entirely and use the mainsail as you return to the marina.
These numbers above are general numbers and since cats don’t heel much it is very important to abide by the wind speed reefing table on your boat.
Jibe (Gybe)
Jibing (gybing) is the downwind version of tacking, meaning you’ll be heading off on another zig-zag 90° journey as you sail out of the bay. But unlike tacking, where you forced the ship’s bow toward the wind, now you’ll be guiding the boat’s stern away from the wind. Here’s how to jibe a catamaran safely and quickly:
- Make sure the traveler is in a center position (or close to center).
- Trim the sail to prevent the boom from swinging in mid-jibe.
- Angle the catamaran so you’re traveling a few degrees off from directly downwind.
- Choose a location in the distance that’s 90° from your current location.
- When the mainsheet feels lighter, bring the boom toward the ship’s center.
- Wait for the leech to rise (the sail’s rear edge).
- Release the mainsheet again.
While jibing can help you stay on course and pick up some speed, it comes with some risks. An uncontrolled boom can rapidly swing and crash into a crew member, cause unpredictable heeling, or damage the rig. Make sure all crew members are ready to jibe before beginning the process.
Reduce Speeds
The physics behind sailing is quite complicated and misconceptions about venturing downwind are common. Thanks to choppy waves (water resistance) and sails (lack of wind resistance), it’s impossible to sail downwind at faster speeds than the wind directly at your aft.
Conclusion
Sailing a catamaran upwind or downwind is more complicated than a calm, Caribbean sailing expedition. Prepare for your next windy escapade by:
- Checking the wind speed and direction via your local weather service
- Practicing reefing, tacking, and cruising skills in calmer conditions
- Experimenting with sail trims, headsail positions, and motor use
- Learning more about spinnakers, screechers, and gennakers
Every gust, knot, and reef will help you hone your catamaran sailing talents and better prepare for less predictable weather. Try to build your confidence and perfect your skills before exposing yourself to harsher conditions.

